Unlocking Metabolic Health: A Science-Backed Guide to the Ketogenic Diet

In the vast landscape of nutritional science, few dietary approaches have generated as much buzz—and as much success—as the ketogenic diet. By dramatically reducing carbohydrate intake and replacing it with healthy fats, this eating plan triggers a unique metabolic state known as ketosis, where the body becomes a highly efficient fat-burning machine.
This guide will move beyond the hype to explore the scientifically-backed benefits, potential considerations, and actionable steps to help you understand if the ketogenic lifestyle is the right choice for your health goals.
What is Ketosis? The Science Behind the Switch
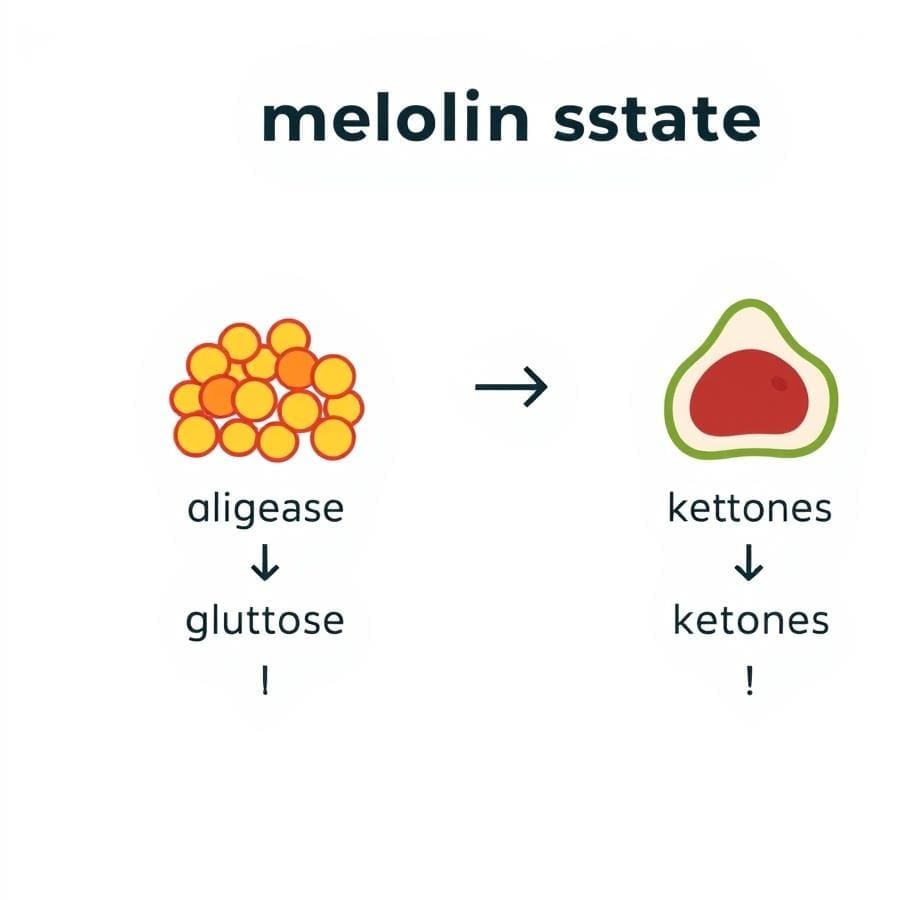
At its core, the ketogenic diet is about changing your body’s primary fuel source. Your body typically runs on glucose, which is derived from carbohydrates.
When you restrict carb intake to 20-50 grams per day, your body’s glucose reserves deplete. In response, your liver begins to break down fats into molecules called ketones.
These ketones then serve as an alternative fuel source for your brain, muscles, and organs. This metabolic state is called ketosis, and it’s the foundation upon which all the diet’s benefits are built.
It’s not about starvation, but rather a metabolic switch from a carb-burning to a fat-burning engine.
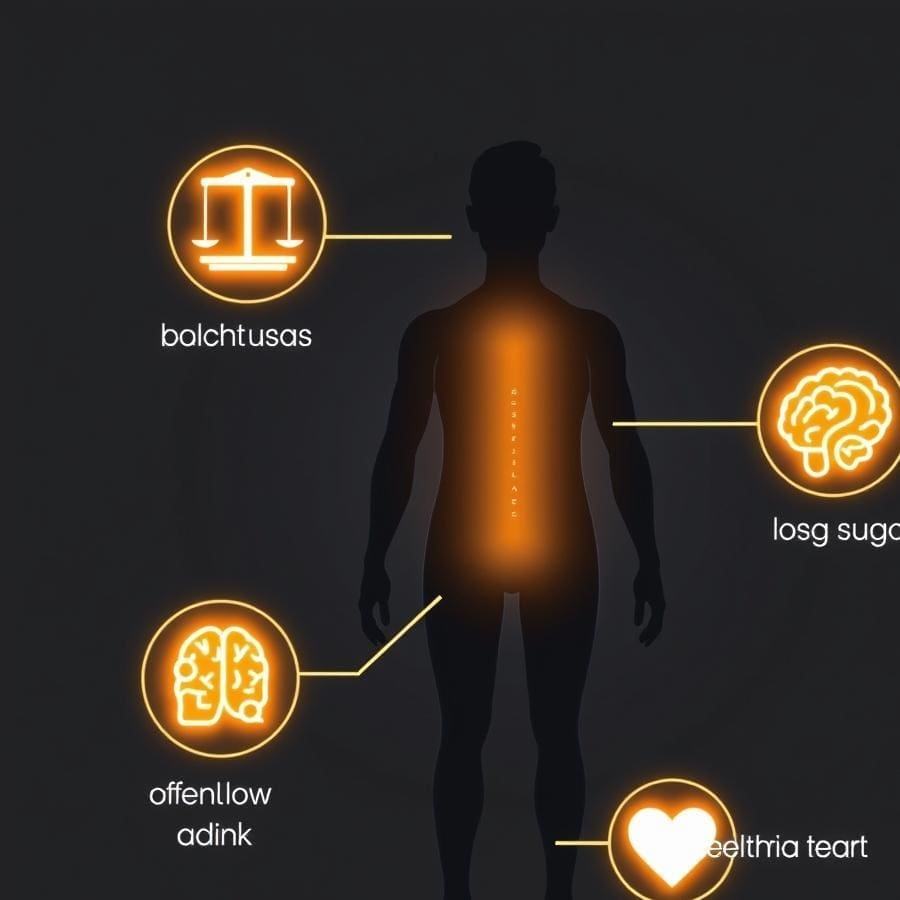
More Than Weight Loss: The Wide-Ranging Health Benefits
While highly effective for weight loss, the advantages of a well-formulated ketogenic diet extend much further. According to research published in Nutrition & Metabolism, the diet is highly effective for improving glycemic control, making it a powerful strategy for managing type 2 diabetes.
Furthermore, many individuals report a significant boost in mental clarity and a reduction in ‘brain fog,’ a benefit that can be complemented with practices like mindfulness meditation for stress reduction, as the brain can run very efficiently on ketones. Other documented benefits include improved triglyceride levels, increased HDL (good) cholesterol, and potential neuroprotective effects, with research from institutions like Johns Hopkins highlighting its role in managing conditions like epilepsy.
How to Start Keto: A Practical Beginner’s Guide

Starting a ketogenic diet requires planning. The key is to build your meals around a foundation of healthy fats (avocado, olive oil, coconut oil), moderate protein (fatty fish, poultry, eggs), and low-carbohydrate vegetables (leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini).
It’s essential to eliminate sugar, grains, and starchy vegetables. Finding keto-friendly alternatives, like a good grain-free granola recipe, is key to long-term success. To combat the ‘keto flu’—a temporary set of symptoms like headaches and fatigue as your body adapts—prioritize hydration and ensure you’re getting enough electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium.
A successful start involves cleaning out your pantry, creating a simple meal plan, and focusing on whole, unprocessed foods.
Conclusion
The ketogenic diet presents a compelling, evidence-based approach to improving metabolic health, managing weight, and enhancing cognitive function. While it demands a significant lifestyle adjustment, its potential rewards are substantial.
By focusing on nutrient-dense foods, staying hydrated, and listening to your body, you can safely and effectively leverage the power of ketosis. As with any significant dietary change, consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is a crucial first step to ensure the approach is tailored to your unique health needs.
